The Ecological Footprint of Ecotourism Packages
Monitoring the Ecological Footprint of ecotourism packages: a sustainable way to discover the protected areas of the Mediterranean region. In 2017, Global Footprint Network began a collaboration with IUCN Med (International Union for Conservation of Nature) and the MEET Network (Mediterranean Experience of Ecotourism) on DestiMED, an Interreg MED-funded project that brings together a network of 13 protected areas in six Mediterranean countries. The goal of the project was to develop and manage ecotourism packages that benefit conservation, while measuring and reducing their environmental impact using the Ecological Footprint framework.
In 2017, Global Footprint Network began a collaboration with IUCN Med (International Union for Conservation of Nature) and the MEET Network (Mediterranean Experience of Ecotourism) on DestiMED, an Interreg MED-funded project that brings together a network of 13 protected areas in six Mediterranean countries. The goal of the project was to develop and manage ecotourism packages that benefit conservation, while measuring and reducing their environmental impact using the Ecological Footprint framework.
The MEET Network monitors the quality and sustainability of ecotourism products across the Mediterranean using their ecotourism standards which include resource consumption as measured by the Footprint. This important monitoring process aims to ensure the best balance between offering high-quality services and maintaining a low Ecological Footprint. The ultimate goal is to create tourism products that inspire transformative nature experiences, environmental consciousness, and cultural exchange — the kind of offering that will appeal to the growing market of vacationers who care about reducing their Footprint while visiting a destination.
 In 2019, the follow-up project DestiMED PLUS was launched with the goal of strengthening the achievements of DestiMED. As a part of DestiMED PLUS, project collaborators have:
In 2019, the follow-up project DestiMED PLUS was launched with the goal of strengthening the achievements of DestiMED. As a part of DestiMED PLUS, project collaborators have:
- tested the Ecotourism Footprint Calculator in nine additional protected areas in the Med,
- upgraded sustainability assessment standards by including new sustainability components, such as socioeconomic, governance, and conservation indicators,
- built a user-friendly monitoring platform (now in development) so the tools required to manage and monitor ecotourism packages can be compiled into in a single interface, and
- strengthened the governance and networking structure surrounding the MEET Association so that the Association can continue to operate autonomously after the project is completed.
The Ecological Footprint of Ecotourism Packages
To assess the Ecological Footprint of ecotourism packages, the Footprint methodology is customized to track the resource consumption of all services provided to tourists including: accommodation; food and drinks; mobility and transfers; activity and services. The assessment is conducted annually to help the local ecotourism group of businesses and public authorities understand and address the impact of their ecotourism products while ensuring their high quality.
Results from DestiMED show that food and drinks make up the largest component of the ecotourism packages’ Ecological Footprint. This is due to the large amount of fish and meat products consumed as protein-based diets have a larger Footprint compared to plant-rich diets. Additionally, the food’s place of origin contributes to the Footprint because food produced farther away requires more transportation, thus a larger Footprint. Food produced on site of consumption or sourced locally (within a 60-km radius) helps ensure a lower Footprint and provides an authentic experience of the local and traditional cuisine.
Ecological Footprint of Ecotourism Packages
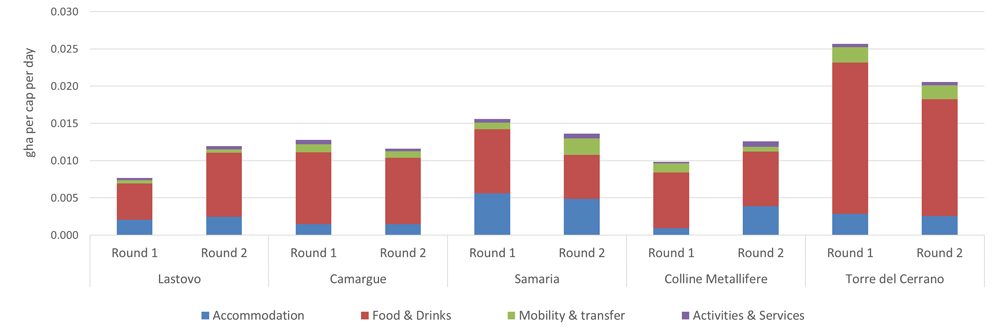
During DestiMED project testing, some ecotourism packages’ Footprints increased while others decreased between the two Footprint assessments (as shown in the figure above). This is because MEET ecotourism packages are based on a range of sustainability standards including quality, economic, social, and cultural aspects. Refinements of the ecotourism packages for the second Footprint assessment had to consider, and balance, both the quality satisfaction feedback by industry experts and Global Footprint Network’s recommendations for Footprint reduction. This highlights the critical balance between offering high-quality tourism and low impact (i.e. high sustainability) ecotourism packages. For full details on the ecotourism packages which were assessed as a part of DestiMED, see Mancini et al., 2022.

Solutions for a Low Tourism Footprint
Results from the DestiMED project illustrate that a low Ecological Footprint of tourism can be achieved by:
- Staying at small-scale, family-run, local and traditional housing accommodations, preferably with renewable energy sources in place. Although large hotel chains are often very resource efficient because of economies of scale, these small-scale hotels will reduce the accommodation Footprint by as much as 48%, Global Footprint Network found.
- Eating food sourced locally or regionally, offered through the typical Mediterranean diet providing an abundance of vegetables and grains, and less animal protein-based products (non-endangered fish-based products and non-intensive meat based-products). Buying local and organic food products improves each meal with a tasty Footprint reduction of 5%, Global Footprint Network found. This can really add up over the course of a trip!
- Considering the quantity of food consumed: light and balanced dishes are favored over lush, bountiful, and never-ending banquets.
- Traveling “slow” by using alternative and motor-free modes of transportation as much as possible. Walking, as well as using bikes, kayaks, horses, or even public transit, is preferred to carbon-intensive transportation. An electric vehicle will help reduce the Footprint by 40-50%, Global Footprint Network found, and a bike ride means no Footprint at all!
- Enjoying carbon-free activities that allow tourists to enjoy the slow pace of the natural areas they are visiting and re-discover the original rhythm of nature.
Daily Footprint on Ecotourism Vacation vs. Daily Footprint at Home
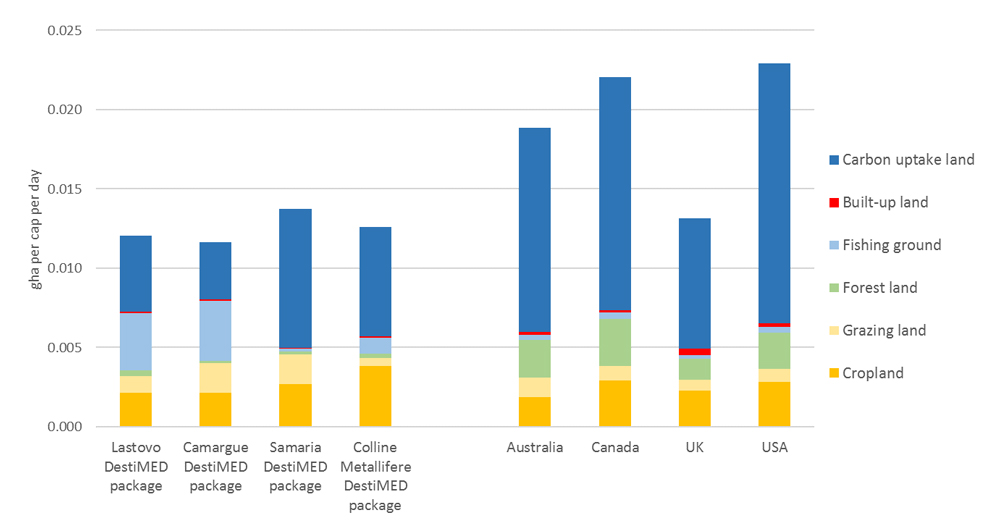
By choosing ecotourism packages, visitors from many countries often have a lower daily Ecological Footprint than they do at home. This DestiMED analysis does not include the Footprint of international travel and further analysis can provide a more comprehensive view on the global impact of tourism. Learn more about the tourism industry’s global carbon emissions in Lenzen et al., 2018.
Daily Ecological Footprint on Ecotourism Vacation vs. at Home


Ecotourism Footprint Calculator
Protected Areas and tour operators can now use an industry-specific online calculator to assess and manage the Ecological Footprint of ecotourism packages. The Ecotourism Footprint Calculator was developed by the DestiMED Project consortium, building on Global Footprint Network’s data and methodology. The tool was recognized for fostering sustainable tourism practices in a European Travel Commission report.
MEET Network
In 2019, Global Footprint Network became member of the board of Directors of the MEET Network whose aim is to develop, manage and promote high-quality ecotourism packages while monitoring their impact through Ecological Footprint assessments. The MEET products offer an alternative tourism experience in and around protected areas of the Mediterranean region.
Ecotourism Course
IUCN Med, Global Footprint Network and the MEET Network, with support from MAVA Foundation, developed a free online course teaching the participatory process of creating ecotourism experiences in and around Mediterranean Protected Areas. Course attendees are also introduced to the concept of the Ecological Footprint and learn how it is used to support ecotourism development and monitoring.

Ecotourism experiences now available with Intrepid Travel
Ecotourism packages from the DestiMED project will now be available to a wider global market thanks to an exclusive new partnership with Intrepid Travel, a global travel brand certified as a B corporation. The multi-day experiences aim to immerse travelers in local nature and culture showing them a different side of what the biodiversity rich Mediterranean region has to offer.


